News Releases
The press releases on this website are provided for historical reference purposes only.
Please note that certain information may have changed since the date of release.
October 9, 2024
Sony Unveils New Technologies to Advance Autonomous Mobile Robots
Five Papers Accepted at IROS 2024, the Top Conference in AI and Robotics
Tokyo, Japan — Sony Group Corporation (Sony Group) today announced that five research papers on robotic mobility published by Sony Group and Sony Interactive Entertainment Inc. (SIE) have been accepted at the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2024, one of the top international conferences in the fields of AI and robotics. The research reported in these papers focused on developing autonomous robots that can move and act in a variety of environments.
Under Sony's purpose to "fill the world with emotion, through the power of creativity and technology," Sony is engaged in research and development (R&D) seeking to create a variety of technologies that unleash people's creativity. Robotics is a real-world application area where Sony can combine its own developments in its core technologies — AI, sensing, and digital virtual world technology. Sony will continue to conduct R&D in fundamental technologies and harmonize various technical fields to provide new Kando (emotion) experiences and contribute to building a more sustainable society.
List of Papers
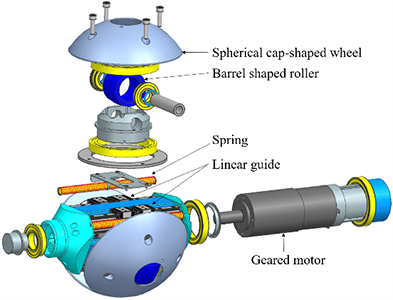
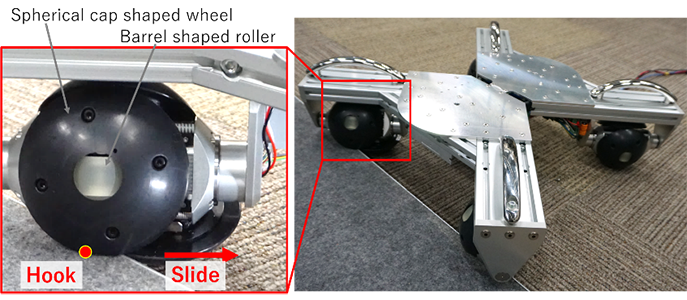
Development of Passive Transformable Omnidirectional Spherical Wheel
Sony Group has conducted research on a six-wheeled robot that can achieve highly efficient movement by switching between wheeled locomotion on flat surfaces and legged locomotion on uneven terrain. To expand the capability of wheeled locomotion, it is crucial to design a wheel mechanism that can stably traverse steps and obstacles. To address this, Sony Group has developed the Passive Transformable Omni-Ball (PTOB), a motor-embedded omnidirectional wheel that can automatically change its shape when encountering a step. This technology has the potential to contribute not only to the evolution of wheeled-legged robots, but also wheeled vehicles such as wheelchairs and carts. This paper has been nominated as a finalist for Best Paper Award on Robot Mechanisms and Design at IROS 2024.
Authors: Kazuo Hongo (Sony Group Corporation), Takashi Kito, Yasuhisa Kamikawa, Masaya Kinoshita, and Yasunori Kawanami
Reference: [2403.14160] Development of a Compact Robust Passive Transformable Omni-Ball for Enhanced Step-Climbing and Vibration Reduction
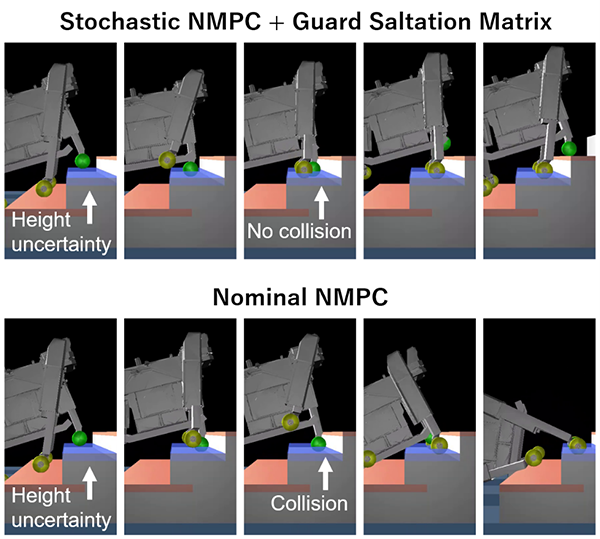
Robustifying Model-Based Locomotion via Zero-Order Stochastic Nonlinear Model Predictive Control with Guard Saltation Matrix
Legged robots have to take safe actions even when there are uncertainties in perception of the surrounding environment. Conventional model-based methods are not easily able to incorporate such uncertainties into motion generation. Instead, much engineering effort had to be made to tune various control parameters to ensure safety. In this research, Sony Group developed a method to predict the future uncertainty of motion while taking environmental uncertainties into account using a guard saltation matrix. By combining this method with optimization-based motion generation, robots can generate safe whole body motion (e.g., leg movements and contact positions) even with imperfect measurements of the surrounding environment.
Authors: Sotaro Katayama (Sony Group Corporation), Noriaki Takasugi, Mitsuhisa Kaneko, Norio Nagatsuka, Masaya Kinoshita
Reference: [2403.14159] Robustifying Model-Based Locomotion by Zero-order Stochastic Nonlinear Model Predictive Control with Guard Saltation Matrix
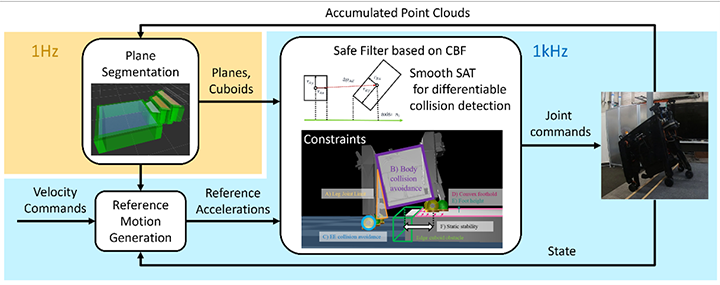
Real-Time Perceptive Motion Control Using Control Barrier Functions with Analytical Smoothing for the Six-Wheeled-Telescopic-Legged Robot Tachyon 3
To adaptively move over various environments, robots have to generate optimal motions using on-the-fly environmental perception in real-time. However, it has been a challenge to compute the optimal motion that t that avoids any collision with surroundings in a sufficiently quick computational time. To address this, Sony Group has developed a new collision detection technology called the Smooth Separating Axis Theorem. By combining this with a safety-critical control method, the Control Barrier Function, the robot can generate safe and smooth motions to place its legs in safe areas within a 1-millisecond computation time.
Authors: Noriaki Takasugi (Sony Group Corporation), Masaya Kinoshita, Yasuhisa Kamikawa, Ryoichi Tsuzaki, Atsushi Sakamoto, Toshimitsu Kai, and Yasunori Kawanami
Reference: [2310.11792] Real-time Perceptive Motion Control using Control Barrier Functions with Analytical Smoothing for Six-Wheeled-Telescopic-Legged Robot Tachyon 3
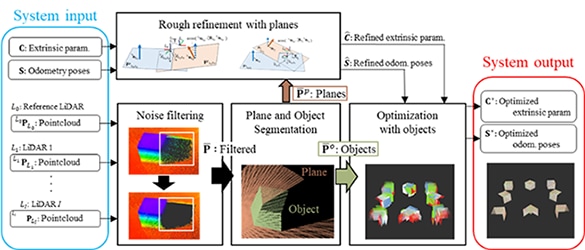
Multi-LiDAR Extrinsic Calibration for Mobile Robots Based on Floor Plane and Object Segmentation
As the use of robots becomes more widespread, everyday hardware maintenance, such as replacements of parts and sensors, will become necessary. After such maintenance, particularly when sensors were re-attached, there is a need to ensure precise adjustments of sensors to their original positions, typically using specialized components such as a calibration board. To address this challenge without the use of specialized components, Sony Group had developed a calibration method to adjust the positions of multiple sensors simultaneously by sensing point clouds on the surrounding floor and objects. Additionally, this method enables high-precision calibration even when there is no overlapping field of view between sensors, which allows for greater flexibility in sensor placement in robot design.
Authors: Shun, Niijima (Sony Group Corporation), Atsushi Suzuki, Ryoichi Tsuzaki, Masaya Kinoshita
Reference: [2403.14161] Extrinsic Calibration of Multiple LiDARs for a Mobile Robot based on Floor Plane And Object Segmentation

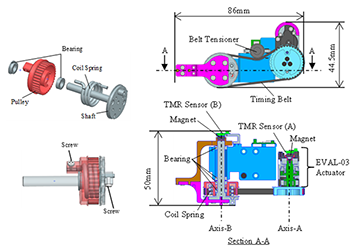
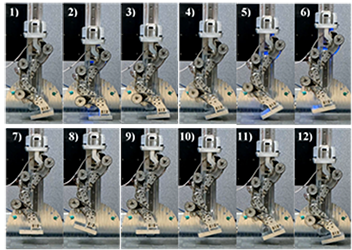
Development of Bidirectional Series Elastic Actuator with Torsion Coil Spring and Implementation to the Legged Robot
SIE explores new possibilities through robotics. To enable robots to perform dynamic movements such as running and jumping, it is necessary to provide shock absorption capabilities as well as increase the output power of the actuators. In this study, SIE has newly developed a small series elastic actuator using a torsion coil spring and implemented it in a single-legged robot. This mechanism enables efficient continuous jumping motions by leveraging the stored elasticity of the spring.
Author: Yuta Koda (Sony Interactive Entertainment Inc.), Hiroshi Osawa, Norio Nagatsuka, Shinichi Kariya, Taeko Inagawa, Kensaku Ishizuka
Reference: [2409.15791] Development of Bidirectional Series Elastic Actuator with Torsion Coil Spring and Implementation to the Legged Robot
About IROS 2024
IROS is the world's largest international conference on robot technology and is co-sponsored by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the Robotics Society of Japan (RSJ).
- Date: Monday, October 14, to Friday, October 18, 2024
- Venue: Abu Dhabi National Exhibition Centre (ADNEC), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Pre-registration is required to attend the conference. For more details, please visit the official IROS 2024 website (external link).

